
The top 6 challenges of the agricultural industry
(Last update: June 11, 2025)
The agricultural industry faces challenges that threaten stability for all stakeholders and global food security. A ProducePay survey identified the six primary agricultural challenges affecting growers, marketers, and retailers throughout the agricultural supply chain.
These insights are explored in depth in our 2024 Volatility Report, which highlights the key sources of unpredictability in the fresh produce supply chain and their impact.
1. Rising input cost and freight volatility
One of the most significant agricultural challenges today is the rise in input costs. Key essentials such as seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, and fuel have significantly increased in price over the past decade.
In our survey, the availability and cost of inputs were cited as the top challenge impacting business profitability.
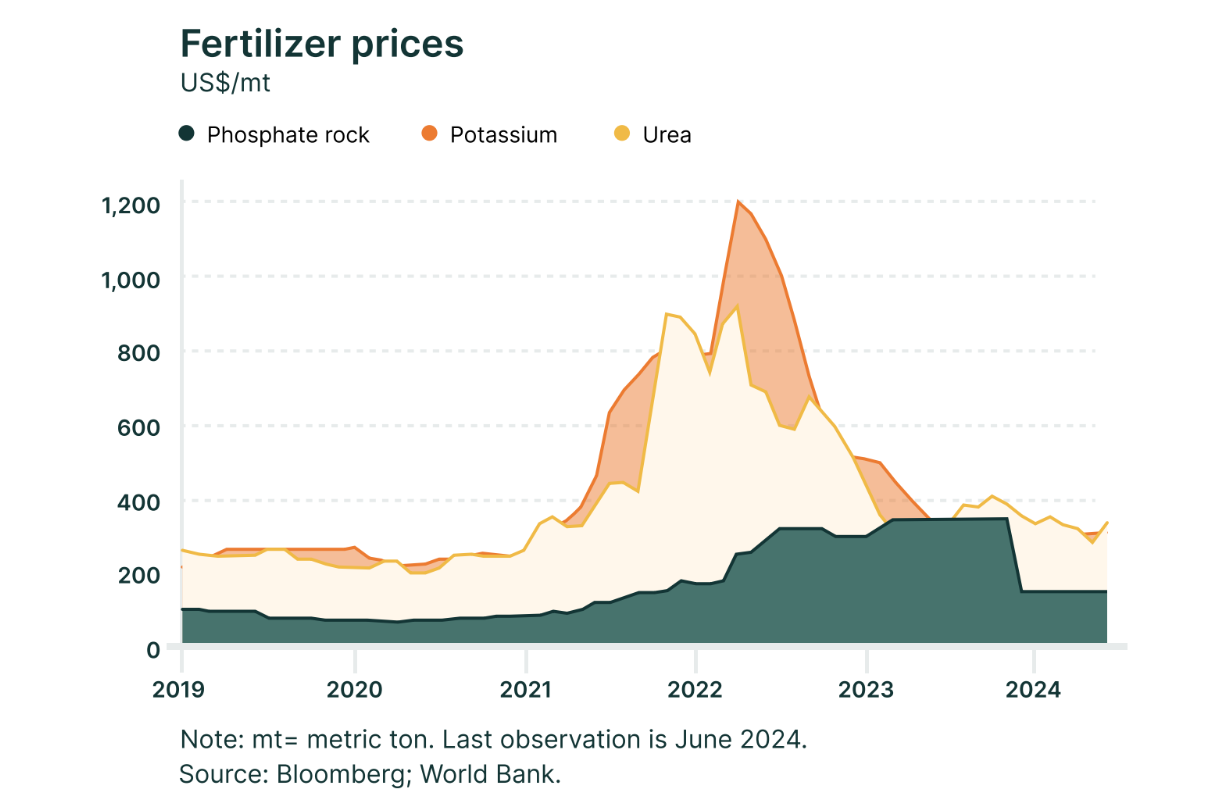
Freight prices have also seen notable fluctuations, driven by persistent challenges in the trucking industry—including a labor shortage that began during the pandemic and remains unresolved—, and increase in fuel prices, particularly following the onset of the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
60% of produce buyers said that freight and storage costs had become more impactful compared to 2023—while 47% of growers agreed.
As these expenses rise, profitability is squeezed across the chain, underscoring the urgency for more efficient operations and smarter logistics planning.
Learn: Strategies to navigate volatility in logistics
2. Farm labor availability and cost
Farm labor remains a persistent concern for agricultural operations. Six out of ten industry stakeholders said that labor costs and availability had worsened. This was particularly true for buyers, with 64% reporting increased difficulty compared to 57% of growers.
Labor-related agricultural issues are influenced by multiple factors like shifting migration policies, which add unpredictability to labor availability. In the U.S., for example, 69% of the crop farming workforce is made up of immigrants.
Meanwhile, rising wages have pushed up production costs, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.55%. Smaller and mid-sized farms are especially vulnerable, as they often lack the resources to compete for skilled labor.
3. Extreme weather and climate disruption
Extreme weather events are becoming more frequent and severe, with major implications for agriculture. The number of global weather events rose from 296 in 2013 to 354 in 2023—a 20% increase.
56% of the survey respondents said that extreme weather increased in 2024 compared to the previous year, ranking it among the top three factors affecting profitability.
Recent events highlight the impact. In Peru, the agricultural sector is still dealing with the consequences of El Niño, which brought record temperatures and disrupted production and now, growers are navigating the shift to La Niña.
In California, unseasonably heavy rains interrupted harvests and exposed weaknesses in water infrastructure last year. Additionally, prolonged drought conditions continue to threaten the long-term viability of fruit and vegetable production in the state.
4. Pricing volatility
Price fluctuations have become one of the most defining agricultural challenges, particularly in fresh produce. According to our research, fresh produce categories experienced 70% annualized volatility at the shipping point in 2024.
More than 10 commodities—including mangos, limes, broccoli, lettuce, cantaloupes, and berries—saw volatility exceed 90% over the same period.
Retail prices have also been unstable, with produce showing an annualized volatility of 47%.
Prices can fluctuate due to supply and demand, weather conditions, or geopolitical events, making predicting these fluctuations challenging. This limits the ability of growers and marketers to forecast revenue and manage risk, affecting every stage of the supply chain.
5. Limited access to capital
Access to capital is a key barrier to growth in the agricultural sector, as many financial institutions remain hesitant to support agriculture, often due to its inherent volatility and the lack of understanding of the industry’s complexities.
According to the survey, marketers who both grow and buy produce were the most affected—60% reported a decline in access to capital, compared to 53% of growers.
Regional differences also emerge. In Mexico, 57% of growers said financial conditions had worsened, while in the U.S., 50% said the same.
Securing farm capital leads to investing in operations, improving efficiency, expanding their operations, or navigating the daily pressures of a dynamic market.
Discover: How buyers are securing produce supply with external financing
6. Food Waste
Food waste is another major agricultural challenge. 70% of industry stakeholders estimate that over 10% of their products are lost or damaged due to inefficiencies in the supply and distribution chain.
This waste is largely driven by the highly fragmented nature of the industry, as misaligned logistics, high number of intermediaries, and poor visibility lead to loss of produce.
Reducing waste is essential for both environmental and financial sustainability, and it demands stronger traceability systems, better coordination, and improved cold chain infrastructure.
A new path through Predictable Commerce
With rising costs, climate disruptions, and price volatility becoming the norm, traditional approaches to trade and planning are not enough. What the industry needs is not just resilience—but predictability.
At ProducePay, we believe the answer lies in fostering Predictable Commerce. Our Predictable Commerce Programs are designed to stabilize the volatility caused by imbalances in supply and demand.
These programs align grower supply with buyer demand to enable a 52-week sourcing strategy with predictable pricing, greater transparency, and reduced waste through integrated planning, real-time visibility tools.
We also provide complementary solutions to support grower success and ensure fulfillment, including Pre-Season working capital to fund crop production and Quick-Pay to accelerate payments to growers.

